Lead from paint, dust, and soil in and around your business or home could be dangerous if not found and dealt with properly to remove lead paint.
This page provides information about potential sources of lead in:
- Older homes and buildings
- Soil, yards, and playgrounds
- Dust
- Products
- Drinking water
- Jobs and hobbies
- Folk remedies
Is your Home or Business Old Enough to be a Lead Hazard?
If your home or business was built before 1978, it’s more likely to have lead-based paint. 1978 is when the U.S. federal government banned consumer uses of lead-based paint, but some states were able to ban it earlier.
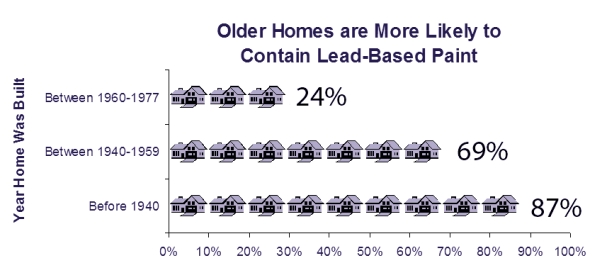
The truth is that lead paint is still present in millions of homes, sometimes under layers of more paint. If the paint is in good shape, the lead paint is usually not a problem. However, if the lead-based paint is deteriorating (peeling, chipping, chalking, cracking, damaged, or damp) is most certainly a hazard and needs immediate attention.
It is possible that lead-based paint can be found on surfaces that children can chew or that get a lot of wear-and-tear, such as:
- Windows and window sills
- Doors and door frames
- Stairs, railings, banisters, and porches
Here are a few tips to reduce the possible sources of lead exposure in older homes and buildings:
- Inspect all painted surfaces and clean up dust frequently with a wet cloth or paper towel. Consult a certified lead professional before beginning any renovation or repair project. Renovation, repair, or painting activities can create toxic lead dust when these surfaces are agitated.
- Don’t track lead dust into the home by wiping and removing shoes before entering the home and placing dust mats both inside and outside of entryways also helps.
- Learn if you have a local lead service line. Contact your water utility or a licensed plumber to determine if the pipe that connects your home to the water main (called a service line) is made from lead. Read more about lead in drinking water.
How to Detect Lead in your Soil, Yards and Playgrounds
Soil, yards and playgrounds become contaminated when exterior lead-based paint from houses or buildings sheds and gets into the soil. Soil may also be contaminated by leaded gasoline in cars, industrial sources, or contaminated sites, including lead smelters. Also important to not that lead is naturally occurring and can be found in high concentrations naturally in some areas.
Lead in soil can be ingested as a result of hand-to-mouth activity that is common for young children and from fruits or vegetables in the soil in the garden. Lead in soil may also be inhaled if suspended in the air or tracked into the house.
Older playground equipment can also contain lead-based paint, and artificial turf and playground surfaces made of shredded rubber can contain lead. Be careful young children don’t eat this rubber or put their hands in their mouth before washing them.
How exactly can you reduce exposures to lead from soils, yards and playgrounds?
- Check the exterior of your home, including porches and fences, for flaking or deteriorating.
- Add doormats outside and inside all entryways and remove your shoes before entering to avoid tracking contaminated soil into the house.
- Wash hands several times a day using soap and water, especially after playing or working outside.
- Plant bushes close to the house to keep children from playing in the soil closest to the home.
Can Lead be Found in House Dust?
Lead in household dust actually results from indoor sources such as old lead-based paint on surfaces that are frequently in motion or bump or rub together (such as window frames), deteriorating old lead-based paint on any surface, or home repair. But it can also be from tracking lead-contaminated soil from the outdoors into the indoor environment.
Here are ways to reduce exposure to lead dust:
- Maintain that all painted surfaces are in good condition.
- Clean frequently using a wet mop, cloth or sponge to reduce the likelihood of chips and dust forming.
- Use a lead-safe certified renovator to perform renovation, repair and painting jobs to reduce the likelihood of contaminating your home with lead dust. Contact Hi-Tech Environmental Renovation today for a professional assessment near you.
Products
Lead products may include painted toys, furniture or toy jewelry, old cosmetics, food or liquid containers, and plumbing materials.
Thankfully, the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) has a comprehensive program on lead in toys including toy jewelry Biting, chewing on or swallowing toys or jewelry that contains lead can cause a child to suffer from lead poisoning. To help protect against risk, CPSC has put protections in place that ban the use of lead in many children’s products. For example:
- In 2004, the threat of lead poisoning from toy jewelry led the CPSC to conduct a voluntary recall of 150 million pieces of metal toy jewelry sold widely in vending machines.
- In 2007, CPSC issued a press release announcing the Fisher-Price recall of 967,000 toys due to lead poisoning hazard.
- Toy jewelry containing unsafe levels of lead has continued to be sold even after CPSC issued guidance to prevent the sale of these products. Other products containing lead have also been recalled, such as crayons, chalk, clothing and children’s products painted with lead-based paint. Learn from CDC what to do if you suspect your child has swallowed toy jewelry.
- CPSC has evaluated whether commercially available lead test kits reliably and accurately detect the presence or absence of lead in consumer products, such as toy jewelry and children’s vinyl toys. Based on this evaluation, CPSC does not recommend that these test kits be used for consumer products.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does recommend a maximum level of lead in cosmetic products. Learn about limits on lead in lipstick and other cosmetics.
Food and liquids stored or served in lead crystal or lead-glazed pottery or porcelain can be toxic because lead can be drawn out of these containers into the food or liquid. Visit the FDA for more information on lead in food and containers.
Lead can enter drinking water when plumbing pipes, faucets and fixtures that contain lead corrode.
How do you Detect Lead in Drinking Water?
The way that lead can enter drinking water is through the corrosion of plumbing materials, especially when your water has high acidity or low mineral content that can actually corrode these lead-containing pipes and fixtures. Any home built before 1986 is more likely to have lead in the pipes, fixtures and even pipe solder.
Fortunately In 2011, changes to the Safe Drinking Water Act reduced the maximum allowable lead content to be a weighted average of 0.25 percent calculated across the wetted surface of pipes, pipe fittings, plumbing fittings and fixtures and 0.2 percent for solder and flux. Interestingly, The most common problem is with lead solder found on brass or chrome-plated brass faucets and fixtures.
How Common is it the Become Contaminated with Lead in Jobs and Hobbies?
When you find yourself working with lead and/or lead-based paint (such as renovation and painting, mining, smelting, batteries, refinishing furniture, autobody, shooting ranges); or with a hobby that uses lead (hunting, fishing, stained glass, stock cars, making pottery) it could definitely cause you to bring lead home on your clothes or body, and contaminate your home. Lead can be found in hunting ammunition, fishing tackle, solder products used in stained glass, weights used in stock cars, dyes and glazes used in pottery and many other job and hobby oriented materials.
How to safeguard yourself if you have a job or hobby where you may come into contact with lead:
- Never put leaded materials (like fishing sinkers, stained glass, pottery clay or glaze) in your mouth.
- Use proper ventilation and equipment when melting lead to cast your own leaded materials such as bullets, sinker, decoys or other metal items.
- Avoid handling food or touching your mouth or face while engaged in working with lead materials, and wash hands before eating or drinking following such activities.
- Be sure to shower and change clothes before entering your vehicle or coming home.
- A good tip is to launder your work and hobby clothes separately from the rest of your family’s clothes.
- Also be sure to keep all work and hobby materials away from living areas.
Do Some Folk Remedies Contain Lead?
You may never have heard of these, but some types of folk remedies, disturbingly, contain lead. These folk remedies such as “greta” and “azarcon are actually used to treat an upset stomach. Some folk remedies for morning sickness, including “nzu”, “poto” and “calabash chalk,” contain dangerous levels of lead and other chemicals. Consuming even small amounts of lead can be harmful. Lead poisoning from folk remedies can cause serious and irreversible illness. Visit the CDC for more information on lead in folk remedies.
Contact Us to ask a question, or to schedule your lead abatement, or asbestos abatement assessment today!
